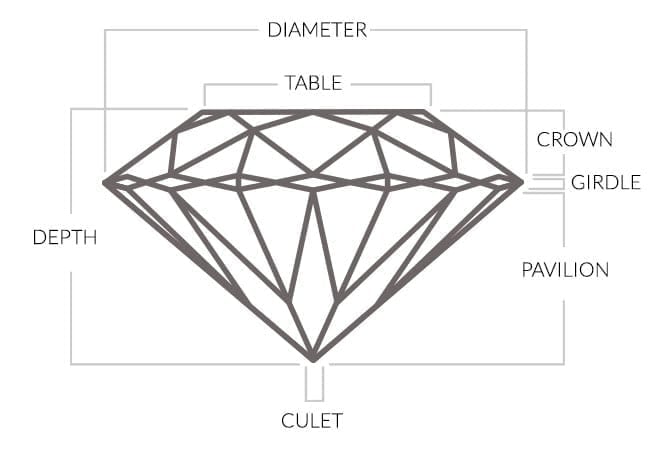
The cutlet is the point at the bottom of the pavilion where the lower facets come together.
Diamonds that are cut too deep or too shallow lose light because the light escapes through the side or bottom. As a result, the diamond becomes less brilliant.
The girdle is the diameter/edge of the diamond. This is where the top portion (crown) meets the bottom portion (pavilion)
The polish of the diamond assists in the overall brilliance of the diamond.
Symmetry refers to how well the facets align with each other.
The facet on the top of the diamond is called the table. The purpose of the table is to allow light into and out of the diamond. Hence, proper table proportion helps to maximize the light reflection and brilliance.
This is a “glow” that emits from some diamonds when they are subjected to an ultraviolet (UV) light. For the most part, diamonds will have fluorescence in two colours, blue and yellow. Some diamonds do not have fluorescence, while others do.
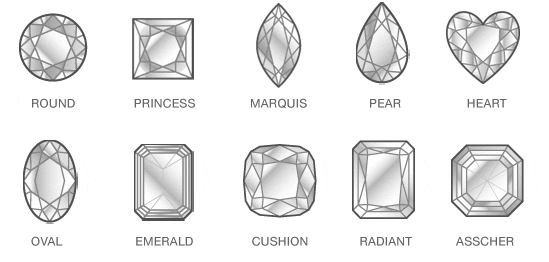
This beautifully unique shape is nearly identical to an Emerald Cut Diamond, except that it is square. Also, this shape has a pavilion that is cut with rectangular facets in the same style as the Emerald Cut Diamond. An Asscher Cut Diamond’s shape highlights the clarity of the diamond.
This unique shape has been popular for more than a century. Cushion Cut Diamonds (also known as “pillow-cut” diamonds) have rounded corners and larger facets to increase their brilliance. These larger facets highlight the diamond’s clarity. Cushion Cut Diamonds are available in shapes ranging from square to rectangular. The length-to-width ratio will determine the diamond’s outline, or what it will look like when viewed from the top.
What makes this shape different is its pavilion, which is cut with rectangular facets to create a unique optical appearance. Due to its larger, open table, this shape highlights the clarity of a diamond. Emerald Cut Diamonds can vary greatly in how rectangular they are. If you prefer an Emerald Cut with a squared outline, look for an Asscher Cut Diamond. The length-to-width ratio will determine the diamond’s outline, or what it will look like when viewed from the top.
The unique look of the Heart Shaped Diamond helps make it a distinctive choice for a variety of diamond jewellery. The length-to-width ratio will determine the diamond’s outline, or what it will look like when viewed from the top.
The shape of a Marquise Cut Diamond can maximize carat weight, giving you a much larger-looking diamond. This brilliant-cut diamond makes fingers appear long and slender. To find the dimension of Marquise you want, look at the length-to-width ratio diagram below. The length-to-width ratio will determine the diamond’s outline, or what it will look like when viewed from the top.
An Oval Cut Diamond has beautiful brilliance that’s similar to a Round Brilliant Cut Diamond. Oval Cut Diamonds are also very popular as their length can accentuate long, slender fingers. The length-to-width ratio will determine the diamond’s outline, or what it will look like when viewed from the top.
This brilliant-cut diamond is also called a teardrop for its single point and rounded end. The unique look of the pear shape helps make it a popular choice for a variety of diamond jewellery. If you choose an elongated pear shape, the length of the diamond creates a subtle slimming effect on the fingers.
Its beautiful brilliance and unique cut makes it a striking diamond for an engagement ring. The Princess Cut Diamond has pointed corners and is traditionally square in shape. Princess Cut Diamonds can vary greatly in how square or rectangular they are.
Trimmed corners are the signature of this diamond, and they help make the Radiant Cut Diamond a popular and versatile choice for jewellery. Radiant Cut Diamonds can vary in their degree of rectangularity. The length-to-width ratio will determine the diamond’s outline, or what it will look like when viewed from the top.
The Round Brilliant Cut Diamond is the most popular and most researched diamond shape available today. For almost 100 years, diamond cutters have been using advanced theories of light behaviour and precise mathematical calculations to optimize the fire and brilliance in a round diamond. A Round Brilliant Cut Diamond will also typically give you more flexibility in terms of balancing cut, color, and clarity grades while still getting the fire and brilliance you want. To maximize the brilliance of a traditional Round Brilliant Cut Diamond, select one with very good proportions, symmetry & polish.




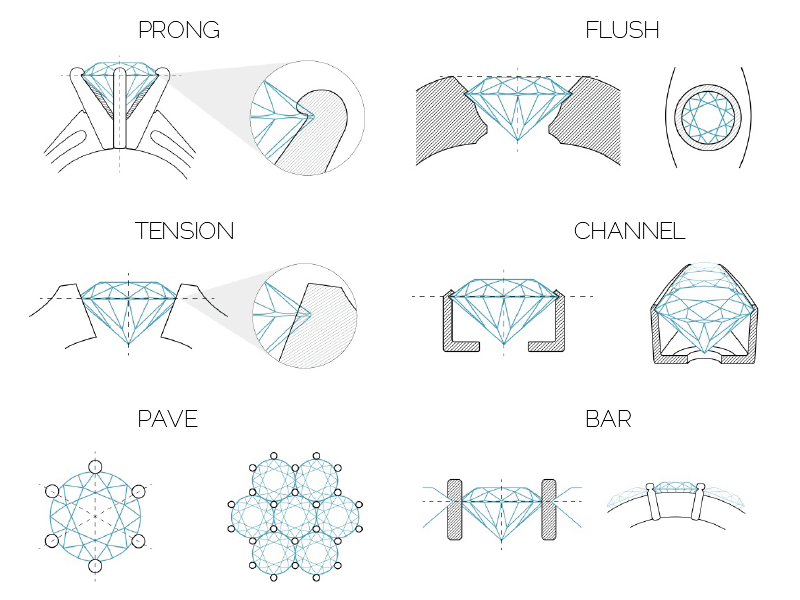
PRONG
One of the most popular setting styles for diamonds, the Prong setting holds a diamond in place with (usually) six prongs. A prong setting shows off the entire diamond, and allows a large amount of light to enter the stone for a dazzling effect. The downside is that you do need to inspect the prongs regularly to ensure they are not damaged, and your stone is more exposed to knocks that could damage it. Because of this a prong setting is not always suited to someone who works with their hands a lot, in these cases a bezel setting may be preferable. The prong setting is used predominantly in engagement rings, but many other pieces that showcase gorgeous diamonds also incorporate it.
FLUSH
The flush setting is similar to a bezel diamond setting, however the top (table) of the stone is the only part exposed. Many jewelers set smaller diamonds flush in the band of a ring, creating patterns and highlights to the band, as well as the main stones. The flush diamond setting is not often used for the main stones of a ring, since it makes the diamond ‘less prominent’.
TENSION
A modern setting style, often used in decorative rings, the tension setting gives a diamond a ‘free’ appearance. A tension setting ring will often have a band of metal that is separated and overlapping, the natural ‘spring’ in the metal will then hold the diamond in place when placed between this metal overlap. While the tension setting looks amazing, it can be easily damaged by sharp knocks, and the ring cannot be resized.
CHANNEL
Channel settings are commonly used in both the band of a ring, and in earrings. Set between two strips of metal, channel diamonds are flush with the metal, which keeps them comfortable to wear, and safe from damage. The channel setting is very popular in wedding rings, where it highlights the centre stone.
PAVE
The pave setting is most often used in ring bands, but can also be found on earrings and pendants. The Pave setting will generally incorporate a large number of small diamonds laid flush with the metal band, very close together but not touching. This creates a solid layer of sparkle, which can make a whole ring sparkle!
BAR
The bar setting is also common in both rings and earrings. Whilst it is similar to the channel setting in use, it looks very different, as the sides of the diamonds lay exposed, and the stones are held in place instead by metal bars between the stones. Many people love this look as the metal contrasts and separates each diamond.